728x90
728x90
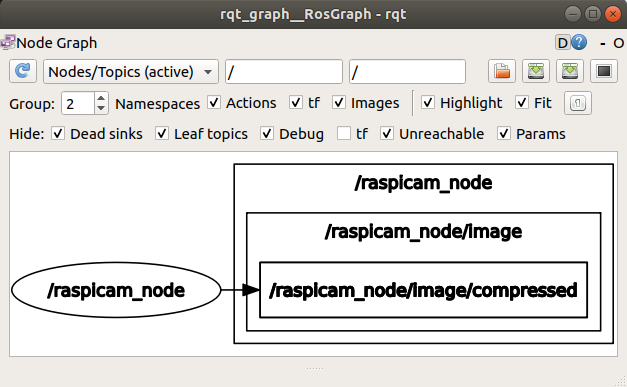
라즈베리파이에서 캠 데이터를 ROS 노드 전송을 이용해 받아온 그래프 형태이다. 이미지 정보는 데이터 노드 내 Image/Compressed 형식으로 존재한다.
728x90

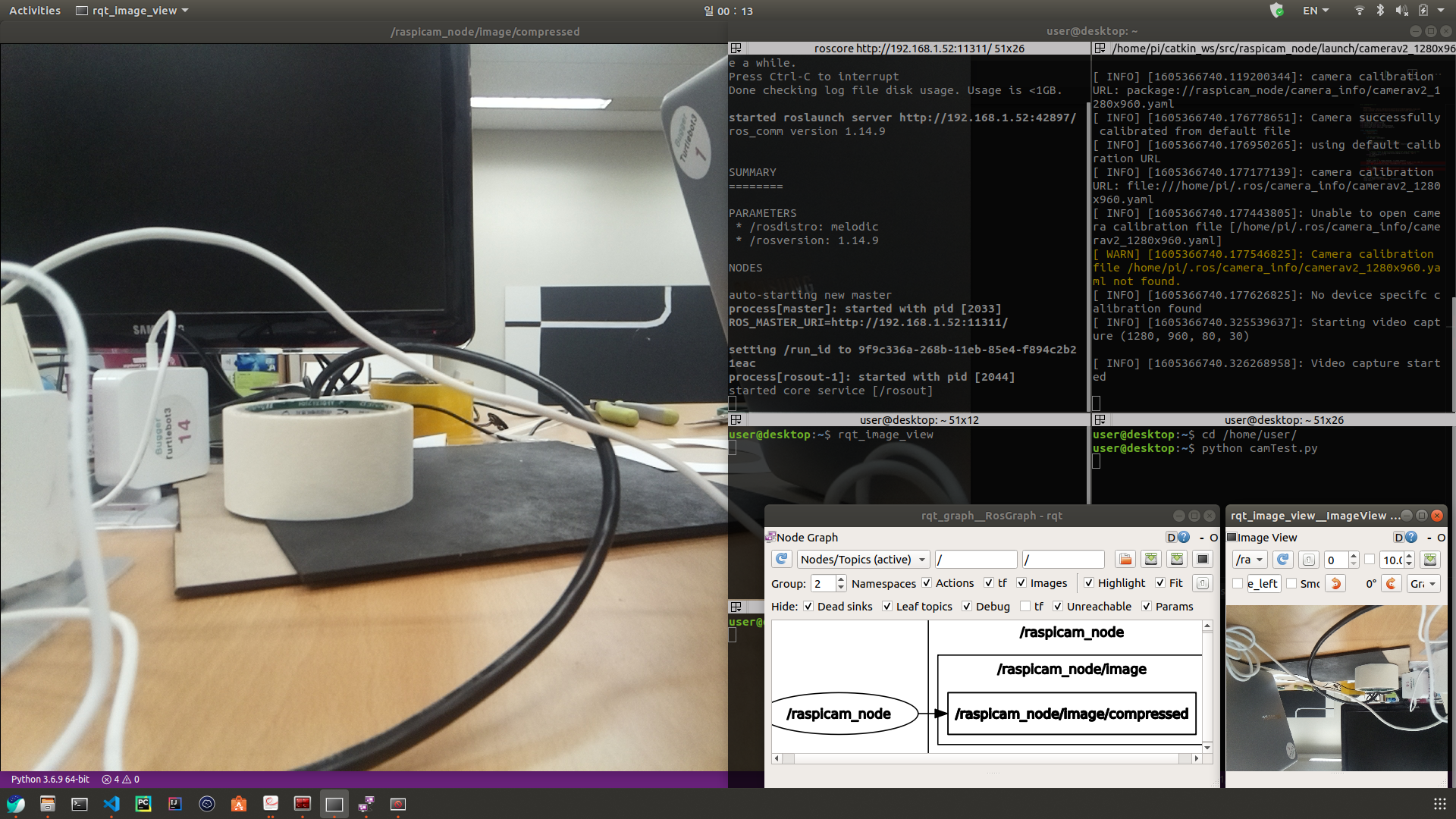
우측 하단 이미지는 터틀봇에서 카메라(터틀봇의 보드는 라즈베리파이를 사용하기 때문에 카메라는 라즈베리캠이다) 데이터를 노드 데이터로 받아와 화면에 띄운 모습니다. 라즈베리파이의 카메라가 반대로 달려있기 때문에 180도 회전되어 출력된다. 이를 아래 파이썬 코드를 이용해 노드 토픽(node topic)의 카메라 데이터를 받아오고 openCV를 이용해 화면에 프로젝션 하는 것이다.
728x90
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
''' References
https://emanual.robotis.com/docs/en/platform/turtlebot3/appendix_raspi_cam/
https://github.com/markwsilliman/turtlebot/blob/master/take_photo.py
by Hoeun Lee (202011353) 2020.11.15. '''
from __future__ import print_function
import sys
import rospy
import cv2
import numpy as np
from std_msgs.msg import String
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from sensor_msgs.msg import CompressedImage
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError
def left_ROI(img):
poly = np.array([
[(0,260),(0,520),(110,520),(110,260)]
])
BG = np.zeros_like(img)
cv2.fillPoly(BG,poly,255)
masked_img = cv2.bitwise_and(img,BG)
return masked_img
def right_ROI(img):
poly = np.array([
[(655,260),(655,490),(745,490),(745,260)]
])
BG = np.zeros_like(img)
cv2.fillPoly(BG,poly,255)
masked_img = cv2.bitwise_and(img,BG)
return masked_img
def HSV_yellow(img):
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
low = np.array([70, 210, 220])
high = np.array([90, 230, 255])
yellowmask = cv2.inRange(hsv, low, high)
return yellowmask
class CompressedImages:
''' Constructor '''
def __init__(self):
# Bridge Instance
self.bridge = CvBridge()
# Get Compressed Image Topic from Subscriber
img_topic = "/raspicam_node/image/compressed"
self.image_sub = rospy.Subscriber(img_topic, CompressedImage, self.callback)
''' Callback Method '''
def callback(self, data):
try:
# Convert Image to OpenCV Format (Compressed Image Message to CV2)
cv_image = self.bridge.compressed_imgmsg_to_cv2(data, "bgr8")
except CvBridgeError as e:
print(e)
# Rotate 180 deg.
height, width = cv_image.shape[0], cv_image.shape[1]
rotatedMatrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((width // 2, height // 2), 180, 1)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(cv_image, rotatedMatrix, (width, height))
''' Image Processing '''
# 노란색 필터
low = np.array([60, 220, 230])
high = np.array([150, 245, 255])
yellowmask = cv2.inRange(dst, low, high)
# Canny Edge Detection
yellowCanny = cv2.Canny(yellowmask, 50, 500, apertureSize=5, L2gradient=True)
# 흰색 필터
low = np.array([248, 250, 248])
high = np.array([255, 255, 255])
whitemask = cv2.inRange(dst, low, high)
# Canny Edge Detection
whiteCanny = cv2.Canny(whitemask, 50, 500, apertureSize=5, L2gradient=True)
# 합치기
lanedtc = cv2.bitwise_or(yellowCanny, whiteCanny)
# 허프 변환으로 선형 도형 검출
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(lanedtc, 2, np.pi/180, 100, np.array([]), minLineLength=10, maxLineGap=30)
# 라인들의 평균 계산
averaged_lines = average_slope(dst,lines)
line_image = display_square(dst,averaged_lines)
combo_image = cv2.addWeighted(dst, 0.6, line_image, 1, 1)
# Show Image
cv2.imshow("/raspicam_node/image/compressed", combo_image)
cv2.waitKey(1)
def display_square(img,lines):
BG = np.zeros_like(img)
if lines is not None:
for line in lines:
x1,y1,x2,y2 = line.reshape(4)
cv2.line(BG, (x1,y1), (x2,y2), (0, 255, 0), 5)
return BG
def average_slope(img,lines):
left_fit = []
right_fit = []
if lines is not None:
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line.reshape(4)
parameters = np.polyfit((x1, x2), (y1, y2), 1)
slope = parameters[0]
intercept = parameters[1]
if slope < 0:
left_fit.append((slope,intercept))
else:
right_fit.append((slope,intercept))
left_fit_average = np.average(left_fit, axis=0)
right_fit_average = np.average(right_fit, axis=0)
left_line = make_coordinates(img, left_fit_average)
right_line = make_coordinates(img, right_fit_average)
return np.array([left_line, right_line])
def make_coordinates(img,coordinate):
slope,intercept = coordinate
y1 = img.shape[0]
y2 = int(y1*(1/5))
x1 = int((y1-intercept)/slope)
x2 = int((y2-intercept)/slope)
print(x1,y1,x2,y2)
return np.array([x1, y1, x2, y2])
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Initialize
camera = CompressedImages()
rospy.init_node('CompressedImages', anonymous=False)
rospy.spin()

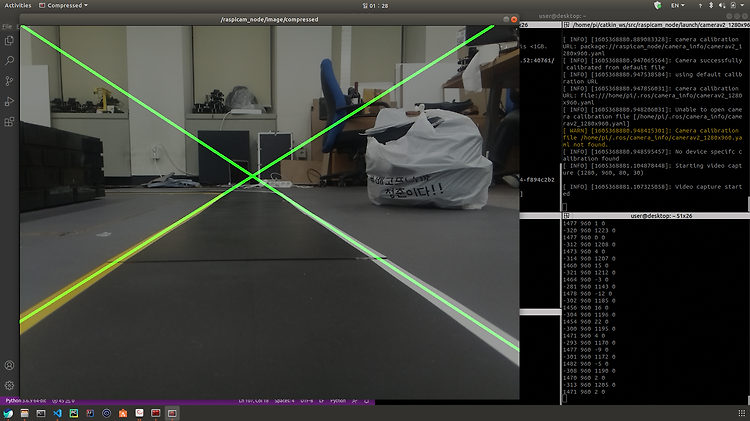
차선을 인식해 화면에 직선을 그려주는 모습이다.
728x90
728x90